Cold fronts generally shown in blue occur where a cold air mass is replacing a warm air mass. Towering clouds and intense storms may form along cold fronts while widespread clouds and rain snow sleet or drizzle may accompany warm fronts.
Frontal Depressions Types Of Fronts Weather Associated And Frontolysis
Air pressure is influenced by the differences between hotter and cooler pockets of air or fronts.

. When neither air mass displaces the other a stationary front develops. When the pockets are very different in temperature they try to mix together creating movement and pressure. As soon as the cold front passes the weather temperature starts becoming cooler and can drop by 4 degree Celsius or even more.
Cold fronts move faster than warm fronts because cold air is denser meaning there are more molecule s of material in cold air than in warm air. The types of clouds that appear during a warm front include Nimbus cumulus and stratus clouds. As changing pressure systems change your blood pressure a host of health consequences can follow Jennifer Vanos an assistant professor in the department of geosciences at Texas Tech said in an.
An increase in the reading on the barometer signifies a rise in the air pressure which leads to good weather while a decrease in this reading means that the air pressure is falling a clear signal that bad weather has arrived or is on the way. There is also an increase in the dew point. They can also bring precipitation.
In a nutshell a cold front is normally characterized by the abrupt arrival of stormy rainy weather that makes a significant impact on a region. Arctic cold fronts can also be accompanied by heavy bursts of snow as they pass through an area that already has subfreezing air in place. Winds may continue to blow into the low pressure zone at the front.
Cold fronts normally occur when a huge mass of cold and chilly air meets a mass of warm air and the chilly air starts advancing on the warm air. Cold fronts often come with thunderstorm s or other types of extreme weather. Big changes in temperature dew point wind speed and direction as well as clouds and precipitation can all come with the passage of a front.
Because the warm air can rise quickly cold fronts can cause cumulonimbus clouds to form with heavy rain and thunderstorms. Along a warm front warm air displaces cold air. Before warm fronts arrives the pressure starts decreasing.
A weather front is a boundary between two air masses. To learn more about the type of front click on the name. A front is a transition zone between two air masses of different densities.
4 Blinding Snow Squalls. Since fronts lie at the edges of contrasting air masses not surprisingly fronts lie in zones with large gradients in temperature and dew point. It can be thought of like the frontline in a battle where the warm air represents one side and its enemy the cold air the other side.
They usually move from west to east. Known as the colorful lines that move across weather maps weather fronts are boundaries that separate air masses of different air temperatures and moisture content humidity. In contrast a warm front takes longer to build up and usually produces more gentle precipitation for more sustained periods.
Two major types of fronts are cold front s and warm front s. Well break down the different types of. The weather at a cold front varies with the season.
It can also bring rain thunderstorms or gusty winds. Behind the front is the cold air mass. It brings rain snow or sleet along with it.
The weather may be cold and clear or only partly cloudy. Warm fronts shown in red occur where warm air replaces cold air. Warm fronts are responsible for huge weather changes.
When they arent very different the atmosphere moves around less -- resulting in usually fewer weather effects. Typically once a storm has moved through a region the barometric pressure should begin to rise again. Fronts are boundaries that separate contrasting air masses.
It is also analogous to a war battlefront where the two air masses. Recalling our study of gradients from earlier in the course I mentioned that areas with large gradients tend to be areas where interesting weather happens and fronts give us a great example. Along a cold front cold air displaces warm air.
The air is unstable so thunderstorms or tornadoes may form. The location where two air masses meet is called a front. A front takes its name from two places.
The types of fronts we discussed previously are cold fronts warm fronts and stationary fronts. It is the literal front or leading edge of air thats moving into a region. Fronts bring changes in temperature dew point winds and pressure.
Learn about the definition and types of weather fronts discover how fronts affect. A weather front is the boundary or transition zone between two air masses that have different characteristics. The cold air will move under the warm air forcing the warmer air to rise quickly.
Weather fronts mark the boundary or transition zone between two air masses and have an important impact on our weatherTo learn more about the history of met. This fairly broad statement does not apply to all frontal occurrences. They can be indirectly observed using current weather maps which can be used to track them as the move across the Earth.
Select each type of front below then click-and-drag to see how it brings different weather conditions. A warm front is where warm air meets cold air. There is usually stormy weather at a weather front.
This mass is drier so precipitation stops. A cold front is where cold air meets warm air.

What Is A Cold Front And How Can It Impact Your Plans Accuweather

Clouds Form Due To Weather Fronts Center For Science Education

The Orographic Effect And Its Impact On The Weather Weather Precipitation Warm Front
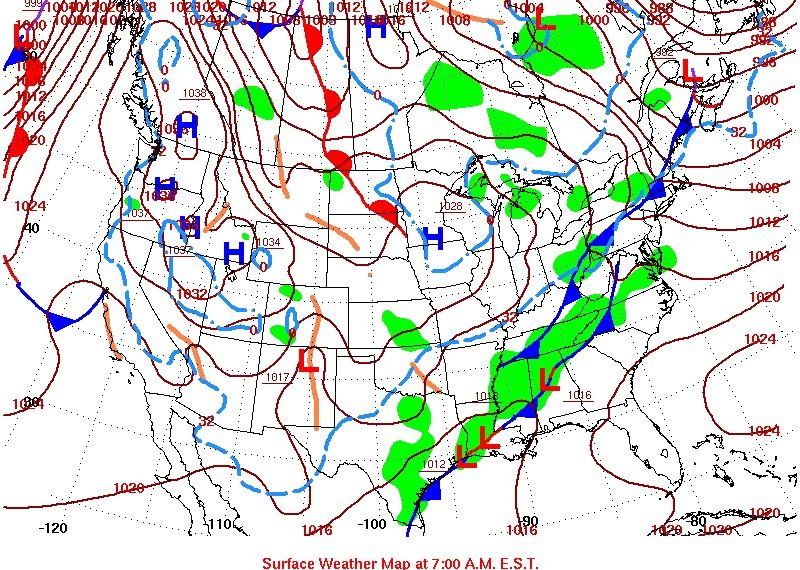
0 Comments